
Bhudhav Hospital
Burns
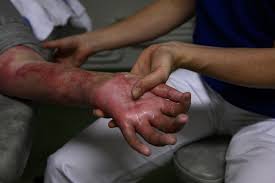
Burns are injuries to the skin and underlying tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. They can vary in severity and require different levels of medical attention.
Types of Burns
First-Degree Burns
- Description: Affect only the outer layer of skin (epidermis). Characterized by redness, minor swelling, and pain.
- Common Causes: Sunburn, brief contact with hot objects.
- Treatment: Cool the burn with running water, apply aloe vera or burn ointment, and cover with a sterile bandage.
Second-Degree Burns
- Description: Affect both the outer layer and the underlying layer of skin (dermis). Characterized by redness, blistering, swelling, and intense pain.
- Common Causes: Scalding liquids, severe sunburn, contact with hot objects.
- Treatment: Cool the burn with running water, do not burst blisters, apply antibiotic ointment, and cover with a sterile bandage.
Third-Degree Burns
- Description: Extend through the dermis into deeper tissues. Characterized by white or blackened, charred skin that may be numb.
- Common Causes: Prolonged exposure to fire, electricity, or corrosive chemicals.
- Treatment: Seek immediate medical attention. Do not immerse in water. Cover the burn with a cool, moist, sterile bandage or cloth.
Fourth-Degree Burns
- Description: Extend through the skin and underlying tissues to affect muscles, ligaments, and bones. Characterized by blackened, charred skin and a lack of sensation due to nerve damage.
- Common Causes: Prolonged exposure to flames or high-voltage electricity.
- Treatment: Seek immediate emergency medical attention. This level of burn requires specialized care and often surgery.
Treatment Options for Burns
First Aid for Burns
- Cool the Burn: Use cool (not cold) water to reduce the temperature of the burn.
- Cover the Burn: Use a clean, non-stick bandage or cloth to protect the burn area.
- Pain Relief: Use over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
Medical Treatments
- Topical Treatments: Antibiotic ointments, silver sulfadiazine cream.
- Dressings: Specialized burn dressings to protect the area and promote healing.
- IV Fluids: To prevent dehydration and maintain blood pressure in severe burns.
Surgical Treatments
- Debridement: Removal of dead tissue to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Skin Grafts: Transplanting healthy skin from another part of the body to cover the burned area.
- Reconstructive Surgery: Procedures to restore function and appearance, such as scar revision and tissue expansion.
